In the realm of nature's intricate tapestry, intricately woven threads bind together the delicate relationship between various life forms and the environments they inhabit. These harmonious ecosystems are the result of eons of evolution, adaptation, and interdependence. However, today, in a world grappling with the repercussions of rapidly changing environmental patterns, this intricate balance faces a daunting challenge.
As our planet experiences substantial alterations in its climatic patterns, a multitude of diverse species find themselves grappling with the consequences. The myriad of transformations that are underway pose a significant threat to both plant and animal life, imperiling the very fabric of biodiversity. The delicate dance of life, once in equilibrium, is now strained, as species struggle to adapt and ecosystems attempt to cope with the onslaught of climatic uncertainties.
The ramifications of these shifts manifest in multifaceted ways. As temperatures rise or fall beyond the accustomed norms, species find their habitats slowly transforming, forcing them to navigate new climates that may not support their survival. The consequences ripple through the food chains, disrupting the well-established dynamics that underpin the intricate tapestry of life. The delicate interplay between predator and prey, symbiotic relationships, and the interconnectedness of flora and fauna begin to unravel, creating a ripple effect that amplifies the challenges faced by individual species and ecosystems as a whole.
In order for us to truly comprehend the gravity of the situation, we must delve deeper into the intricate web of connections that lie within ecosystems. By understanding the delicate balance between species and their environments, we can gain insight into the potential implications of climate change, and the measures necessary to mitigate its impact. Acquiring such understanding is not only a scholarly endeavor but a moral obligation to safeguard the rich tapestry of life that we are fortunate to coexist with on this planet.
The Urgency of Addressing the Crisis to Safeguard Wildlife and Ecosystems

In today's world, an imminent and pressing predicament demands our utmost attention: the dire need to combat the escalating crisis grimly clouding the future of wildlife and ecosystems worldwide. Acutely comprehending the gravity of this situation is paramount if we wish to ensure the preservation of biodiversity for generations to come.
By recognising the urgent necessity to address the environmental challenges unfolding before us, we hold the key to safeguarding the intricate tapestry of life on Earth. The ramifications of our choices, or lack thereof, reach far and wide, permeating ecosystems fragilely adjusted over millennia.
Embracing the responsibility bestowed upon us to mitigate these threats requires understanding the interconnectedness that binds species and habitats together. With unwavering dedication, we can counteract the looming shadows of devastation that threaten to engulf our planet's invaluable natural wonders.
The vitality of proactive measures magnifies as we consider the potential repercussions of inaction. The intricate symphony of ecosystems, with each species playing a crucial role, can become discordant and fragmented, resulting in immeasurable consequences. From the tiniest organisms to awe-inspiring apex predators, the impacts reverberate throughout the intricate web of life, imperiling not only individual species but entire ecosystems.
As stewards of this Earth, we possess the power to steer the tide away from irreversible damage. Our collective actions have the potential to shape a future where ecosystems flourish, wildlife thrives, and biodiversity remains a cherished inheritance for future generations.
The urgency of addressing climate change cannot be understated. Through cohesive global efforts, we can forge a path towards sustainability, rekindling harmony between our actions and the natural world. Time is of the essence, and we must act swiftly and decisively to secure a vibrant and resilient future for our shared planet.
Examining the Devastating Consequences of Altering Patterns in Nature's Diversity
Unveiling the profound outcome of human-induced shifts on the intricate fabric of life's variety has become a pressing matter. As interweaved dynamics oscillate with intensifying global shifts, exploring the dire repercussions of altering patterns becomes imperative.
Understanding the Criticality: The intricate web of life, with its diversity sprinkled across ecosystems, faces a crisis of alarming proportions. The ramifications of modifying nature's delicate balance reverberate across species and habitats, causing profound changes. These disruptions, driven by human-induced alterations, disrupt ecosystems in ways that are difficult to fathom.
The Frailty of Connections: The devastation inflicted on biodiversity cannot be comprehended without recognizing the delicacy of interconnections. Stunningly intricate networks of relationships, from pollinators and plants to predators and prey, are unraveling in a time of drastic change. The consequences extend far beyond individual species, resonating within ecosystems and up the chain, ultimately affecting the very foundation of life's intricate tapestry.
An Eroding Tapestry: As patterns in nature's diversity are reshaped, critical functions begin to erode. The loss of vital species and the disruption of intricate ecological processes have far-reaching consequences that extend beyond immediate implications. The ripple effects, spreading across ecosystems, hold the potential to trigger unforeseen cascades of change, intensifying the peril faced by all forms of life.
Adaptation Under Duress: While resilience and adaptation have long been well-known survival strategies in the biological realm, the pace and scale of current and projected changes pose an unprecedented challenge. The ability of organisms to cope with shifting conditions is tested to the brink as they struggle to keep pace with the altering climate patterns and the rapidly transforming landscapes.
Guardians of Biodiversity: As the severity of the threats becomes increasingly evident, the responsibility to protect and conserve biodiversity lies with humanity. Empowering collective action, mobilizing resources, and implementing sustainable practices are essential to mitigate the devastating impacts of climate change on nature's intricate masterpiece, ensuring its endurance for future generations.
Understanding the Connection Between Climate Crisis and Loss of Habitat
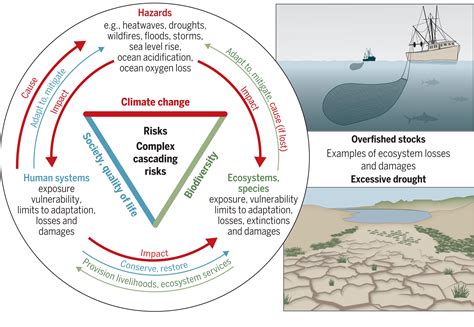
Exploring the intricate relationship between changes in the Earth's climatic patterns and the decreasing availability of suitable living spaces for various species, this section delves into the crucial link between the climate crisis and the alarming loss of natural habitats.
In a world profoundly impacted by global warming and ecological disruptions, the term "climate crisis" encompasses the escalating alterations in weather patterns, temperature fluctuations, and increasing occurrences of extreme weather events. These changes have far-reaching consequences that extend beyond climatic conditions and directly influence the habitat availability for countless species.
The steady rise in global temperatures has led to the melting of polar ice caps and glaciers, resulting in the loss of critical ecosystems that many wildlife species rely upon for survival. Moreover, as warmer temperatures prevail in certain regions, habitats such as forests and wetlands undergo transformations that render them unsuitable for the species they once supported.
- The impacts of the climate crisis also manifest in the form of changes in precipitation patterns, affecting the availability of water sources necessary for flora and fauna survival.
- As habitats shrink or become fragmented due to changes in climatic conditions, species struggle to find suitable areas to nest, breed, and forage for food, leading to a significant loss of biodiversity.
- Additionally, the intensification of extreme weather events, including hurricanes, droughts, and wildfires, further accelerates the destruction of landscapes and habitats, leaving displaced wildlife populations vulnerable and struggling to adapt.
Understanding the interconnection between climate change and the loss of habitat is crucial for implementing effective conservation strategies that mitigate the detrimental impacts on wildlife and promote the preservation of biodiversity. By addressing the factors contributing to habitat loss and implementing sustainable initiatives, we can work towards preserving the delicate balance within ecosystems and protecting the incredible diversity of life on our planet.
The Role of Climatic Shifts in Altering Animal Migration Patterns
Movement is a fundamental aspect of an animal's life. Throughout history, species have adapted their migration patterns in response to shifts in their environment. In recent times, the ever-changing climate has emerged as a significant factor reshaping these patterns. The alterations in temperature, precipitation, and other climatic variables have the potential to disrupt traditional migratory routes and timing, throwing the delicate balance of ecosystems into turmoil.
Changing climates pose both challenges and opportunities for animal migration. The intricate interplay between vast landscapes and species adaptation can be disrupted by the rapid modifications in the environment. As temperatures and weather patterns shift, favored habitats may no longer provide the necessary resources for a species to survive. Consequently, animals may be forced to seek alternative routes or make adjustments to their timing of migration. These changes can have cascading effects on the populations they leave behind and the ecosystems they traverse.
Animals rely on a variety of cues to guide their migration, including celestial cues, magnetic fields, and landmarks. However, in our swiftly changing world, the predictability of these cues can become compromised. For instance, alterations in the climatic conditions can affect the availability of key food sources at particular times, leading to mismatches in migration timing and resource availability. Furthermore, variations in temperature can disrupt internal biological clocks, affecting the ability of animals to accurately time their departure and arrival.
The consequences of altered migration patterns can be far-reaching. In addition to impacting the species directly involved, changes in migration can disrupt the ecological interactions that rely on the timing and movements of these species. Pollination, seed dispersal, and predator-prey relationships are examples of intricate ecological processes that can be drastically influenced by shifts in the migratory behavior of key species.
Understanding the role of climate change in altering animal migration patterns is crucial for effective conservation strategies. As humans continue to alter the planet's climate, it is essential to recognize the repercussions of these changes on wildlife and ecosystems. By comprehending the complexities of animal migration in the face of climate change, researchers and conservationists can work towards implementing measures to mitigate any negative impacts and ensure the preservation of biodiversity.
Rising Temperatures and Escalating Risks of Species Extinction
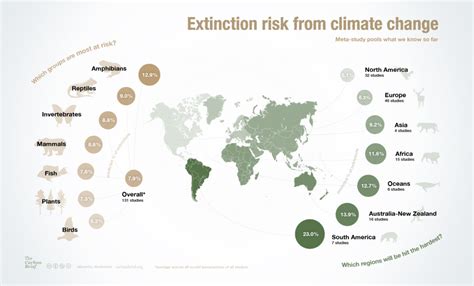
In recent years, the continuing increase in global temperatures has emerged as a significant concern for the survival of various species and has raised alarm bells for the long-term health of ecosystems worldwide. As temperatures rise, numerous species face escalating risks of extinction, thereby threatening the delicate balance of biodiversity.
The upward trend in temperatures has disrupted the natural habitats and biological processes of many organisms, resulting in various consequences for their survival. One of the most immediate impacts is the alteration of species' reproductive patterns and behaviors. As temperatures increase, breeding seasons can shift, affecting the synchronization of reproductive activities among different species. This can lead to mismatches in timing between key biological events, such as the availability of food resources or optimal conditions for reproduction, potentially diminishing the chances of successful reproduction and amplifying the risk of species being unable to adapt and persist.
Furthermore, rising temperatures can also directly affect the physiological functions of organisms. Many species have specific temperature ranges within which their bodies function optimally. When exposed to higher temperatures, these organisms may experience heat stress and metabolic imbalances, compromising their overall fitness and ability to survive. Additionally, increased temperatures can exacerbate the susceptibility of certain species to diseases and parasites, as higher temperatures may boost the reproduction rates or survival rates of these pathogens, placing additional stress on already vulnerable populations.
Another consequence of rising temperatures is the alteration of ecosystems and the distribution of species. As temperature zones shift and previously suitable habitats become less favorable, certain species may be forced to migrate or adapt to new conditions. However, not all species have the same ability to disperse or adapt, resulting in potential range contractions or even local extinctions. This disruption to established ecological patterns can have cascading effects throughout the food chain and further destabilize already vulnerable ecosystems.
Overall, the increasing temperatures associated with climate change pose a significant threat to global biodiversity. By comprehending the risks and understanding the mechanisms through which rising temperatures impact species, we can better inform conservation efforts and develop strategies to mitigate the negative effects of climate change on wildlife and ecosystems. However, urgent action is required to curb greenhouse gas emissions and reduce the rate of temperature rise to safeguard the future of our planet's diverse and irreplaceable natural heritage.
Ocean Acidification: A Quiet Menace to Marine Life and Coral Reefs
Under the relentless assault of a changing environment, our planet's oceans face an insidious and often overlooked threat: ocean acidification. This phenomenon, arising from rising levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, quietly jeopardizes the delicate balance and biodiversity of marine ecosystems and imperils the survival of coral reefs.
As carbon dioxide emissions continue to soar, the world's oceans serve as a major sink for this greenhouse gas. However, this absorption comes at a cost. When carbon dioxide dissolves in seawater, a chemical reaction occurs, leading to the release of hydrogen ions. As a result, the pH of the ocean gradually decreases, causing it to become more acidic.
The ramifications of this process are far-reaching and profound. Ocean acidification disrupts the physiology and behavior of countless marine organisms, from microscopic plankton to majestic coral colonies. It impairs the ability of shell-forming species, such as oysters and clams, to build their protective calcified structures. At the same time, the weakened skeletons of coral reefs are left vulnerable, making these intricate ecosystems more susceptible to erosion and destruction.
The consequences extend beyond the immediate impact on individual species. The intricate interconnectedness of marine ecosystems means that disruptions in one component reverberate throughout the web of life. Reduced biodiversity, as well as the depletion of keystone species, can lead to cascading effects, diminishing the overall health and resilience of these fragile habitats.
The urgency of addressing ocean acidification cannot be overstated. Mitigating this silent menace requires a multifaceted approach, including the reduction of carbon dioxide emissions, the protection and restoration of coastal ecosystems, and the development of innovative strategies to adapt to this rapidly changing world. By understanding the threat posed by ocean acidification, we can work together to safeguard the future of marine life and preserve the vibrant beauty of coral reefs for generations to come.
Climate Change's Impact on Predator-Prey Dynamics and Trophic Cascades
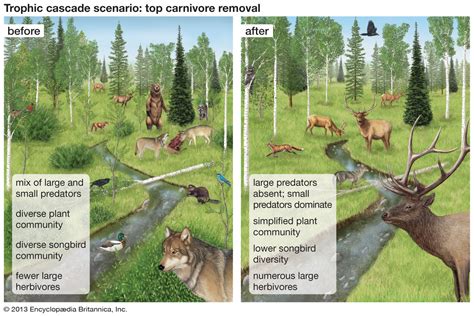
In the midst of a rapidly changing environment, the intricate relationships between predators and prey are being heavily influenced. The consequences of climate change on these dynamics and the resulting trophic cascades are starting to unfold, posing significant challenges to biodiversity.
The shifting climate conditions are altering the distribution and availability of resources, affecting the behavior of both predator and prey species. As temperatures rise or rainfall patterns change, the traditional habitats and ranges of these organisms are also being disrupted. This disruption can lead to changes in migration patterns, breeding cycles, and foraging strategies, ultimately impacting the delicate balance of predator-prey interactions.
Furthermore, the availability and abundance of food sources for predators are being altered due to climate change. As certain plants and animals struggle to adapt to new conditions, the composition and availability of prey species change. This can have cascading effects throughout the food chain, as changes in the abundance or absence of key prey species can impact the survival and reproductive success of predators.
The intricate web of trophic interactions within ecosystems is further exacerbated by climate change. Trophic cascades, where changes in one trophic level affect multiple levels below, become amplified. The consequences of alterations in predator-prey dynamics can ripple through entire ecosystems, affecting not only the species directly involved but also their associated flora and fauna. The loss of top predators or the proliferation of certain prey species can have far-reaching implications for biodiversity and ecosystem functioning.
Understanding and predicting the impact of climate change on predator-prey dynamics and trophic cascades is of utmost importance for effective conservation and management strategies. It requires continuous monitoring, research, and collaboration across disciplines to comprehend the complex ecological consequences and develop appropriate mitigation measures.
Disruptions to Ecosystem Services: How Climate Variations Impact Human Well-being
Exploring the multifaceted consequences of variations in climatic patterns on the welfare of human populations requires a comprehensive understanding of the disruptions to ecosystem services. As climate conditions continue to evolve, alterations in the natural dynamics intricately linked to human well-being are becoming apparent. This section delves into the intricate relationship between changing climatic factors and their implications for the various services ecosystems provide.
The relentless transformations in climate conditions exert a profound influence on the provisioning, regulating, and cultural services ecosystems offer humanity. Deviations in temperature regimes, precipitation patterns, and the frequency of extreme weather events alter the availability of essential resources required for sustenance. These variations can disrupt food production systems, compromise water availability, and increase the vulnerability of communities to natural disasters, ultimately compromising human health and livelihoods.
Furthermore, the intricate interconnectedness of ecosystems means that shifts in climate can trigger a cascade of consequences that impact the regulating services vital for maintaining environmental stability. Changes in temperature and precipitation regimes can disturb the delicate balance of nutrient cycling, pollination processes, and disease regulation, diminishing the overall resilience of ecosystems. Consequently, the well-being of human populations reliant on the essential functions performed by these ecosystems can be profoundly affected.
| Provisioning Services | Regulating Services | Cultural Services |
|---|---|---|
| Food production | Nutrient cycling | Aesthetic and spiritual value |
| Water resources | Pollination | Recreational and tourism opportunities |
| Raw materials | Climate regulation | Historical and cultural heritage |
The consequences of climate variations on cultural services are equally noteworthy. Changes in climate can significantly impact the aesthetic and spiritual value derived from ecosystems, as well as recreational and tourism opportunities associated with natural landscapes. Furthermore, alterations to climate regimes can disrupt historical and cultural heritage sites, eroding the sense of identity and connection to the land, thus impacting the well-being of communities.
Overall, comprehending the disruptions to ecosystem services caused by climate variations is crucial for understanding the intricate ways in which human well-being is influenced. By acknowledging the intricate connections between climate, ecosystems, and human populations, informed decisions can be made to mitigate the adverse effects and foster resilience in the face of a changing climate.
The Role of Global Warming in Shifting Ecological Systems and Invasive Species
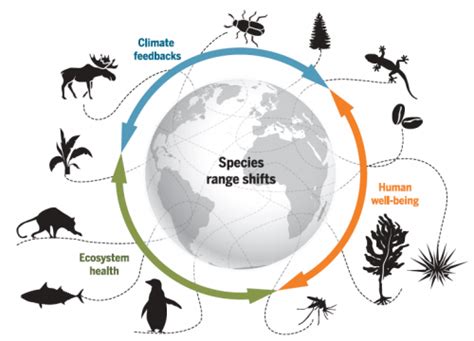
As our planet undergoes significant temperature fluctuations, it has a profound effect on the delicate balance of ecosystems and the proliferation of non-native species. The changing climate acts as a catalyst, bringing about modifications in various habitats and subsequently altering the interactions between organisms and their environment. This section will delve into the crucial role that global warming plays in the shifting of ecological systems and the introduction and spread of invasive species.
The Shift in Ecological SystemsOne of the manifestations of climate change is the redistribution and alteration of ecosystems worldwide. The rising temperatures and shifting precipitation patterns disrupt the equilibrium within habitats, forcing species to adapt or relocate. Consequently, there is a noticeable rearrangement of plant communities, animal distributions, and ecological processes. For instance, certain species may extend their ranges towards the poles in response to warmer temperatures, while others may experience habitat fragmentation or loss due to changing conditions. These transformations can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem, leading to changes in species composition, food web dynamics, and overall biodiversity. |
Invasive Species and Climate ChangeClimate change also poses a significant risk in facilitating the spread of invasive species. Warmer temperatures and altered precipitation patterns create new opportunities for non-native species to establish themselves in previously unsuitable environments. The increased frequency and intensity of extreme events, such as storms and droughts, further aid the dispersal of these invasive organisms. Once introduced, invasive species can outcompete native species for resources, disrupt natural ecosystems, and even cause economic and ecological damage. Understanding the interplay between climate change and the spread of invasive species is crucial for effective conservation and management efforts. |
Wildlife Conservation in the Face of Changing Environments: Strategies for Adaptation and Mitigation
As the world experiences transformations in its natural habitats and climates, it becomes crucial to address the challenges and opportunities that arise for wildlife conservation. This section explores various strategies aimed at helping wildlife adapt and mitigate the effects of these changing environments, ensuring their long-term survival and the maintenance of healthy ecosystems.
The first strategy focuses on habitat preservation and restoration, recognizing the importance of providing suitable environments for wildlife to thrive. By conserving and rehabilitating habitats, we can help create resilient ecosystems that can better withstand the impacts of changing climates. This includes protecting critical areas, such as breeding grounds and migration routes, as well as restoring degraded habitats to their former functioning states.
Another key strategy is promoting genetic diversity within animal populations to enhance their adaptive capacity. By maintaining diverse gene pools, wildlife species are more likely to possess the necessary genetic variations and adaptations to survive and reproduce in changing environments. This can be achieved through captive breeding programs, reintroduction of locally extinct species, and connecting fragmented populations to facilitate gene flow.
Furthermore, the establishment of protected areas and wildlife corridors is crucial for facilitating species movement and addressing the challenges posed by habitat fragmentation. Protected areas provide safe havens for wildlife, enabling them to disperse, adapt, and find suitable habitats as conditions change. Meanwhile, wildlife corridors connect these protected areas, allowing for the movement and exchange of individuals between populations, thus promoting genetic diversity and reducing the risk of local extinctions.
Additionally, sustainable land and resource management practices play a significant role in wildlife conservation efforts. By integrating conservation and ecosystem-based approaches into land-use planning and management, we can minimize the negative impacts of human activities on wildlife and their habitats. This involves implementing measures to reduce habitat destruction, pollution, and unsustainable exploitation of resources, while promoting sustainable practices that maintain the integrity of ecosystems.
Lastly, fostering public awareness and engagement is crucial for the success of wildlife conservation in the face of climate change. Education and outreach programs play a key role in promoting understanding, empathy, and support for conservation efforts. By involving local communities, stakeholders, and policymakers in decision-making processes, we can enhance the effectiveness and sustainability of conservation initiatives, ultimately leading to a better-managed and more resilient natural world.
| Strategies for Wildlife Conservation in the Face of Climate Change |
|---|
| Habitat preservation and restoration |
| Promotion of genetic diversity |
| Establishment of protected areas and wildlife corridors |
| Sustainable land and resource management practices |
| Fostering public awareness and engagement |
The Importance of Global Collaboration in Combating Environmental Change and Safeguarding Ecological Diversity

International cooperation is essential in addressing the challenges posed by environmental change and protecting the variety of life on Earth. Bringing together nations across the globe is crucial in our collective efforts to mitigate the effects of transformations in our natural world.
Achieving effective international collaboration requires a shared understanding and acknowledgement of the urgency and magnitude of the issues at hand. With diverse ecosystems and wildlife facing unprecedented threats, it is paramount that countries unite their efforts to develop and implement strategies that pave the way towards a sustainable future.
Collective action is necessary to exchange knowledge and best practices, harness resources, and establish global policies that can effectively tackle climate-related challenges. Sharing scientific research and data on the impact of ecological disturbances can help identify vulnerable areas and develop targeted conservation measures.
- Enhancing interdisciplinary collaborations: By fostering partnerships between scientists, policymakers, and local communities, we can better understand the interconnections between climate change and biodiversity loss. Through joint research and knowledge exchange, innovative solutions can be developed to address the multifaceted environmental challenges we face.
- Promoting sustainable practices: Encouraging sustainable land-use practices, responsible consumption, and renewable energy sources are key to minimizing the negative impacts of climate change. By sharing success stories and promoting sustainable development models, countries can collectively mitigate the threats to wildlife and ecosystems.
- Building resilient ecosystems: Through international cooperation, efforts can be made to restore and protect vital habitats, such as forests, coral reefs, and wetlands. By enhancing the resilience of ecosystems, we can safeguard biodiversity and ensure the long-term survival of numerous species.
- Engaging stakeholders and fostering public awareness: Collaboration on a global scale can help raise public awareness about the importance of biodiversity conservation and the need for climate action. By involving individuals, communities, and organizations, we can inspire collective behavioral changes and garner widespread support towards environmental sustainability.
In conclusion, global collaboration is fundamental in addressing climate change and safeguarding biodiversity. By pooling resources, knowledge, and expertise, countries can ensure a more sustainable and resilient future for wildlife and ecosystems worldwide.
FAQ
What is climate change and how does it affect wildlife and ecosystems?
Climate change refers to long-term changes in temperature, precipitation, wind patterns, and other aspects of the Earth's climate system. It affects wildlife and ecosystems by disrupting their natural habitat and altering their food sources. Rising temperatures can also lead to the extinction of certain species.
How does climate change threaten biodiversity?
Climate change threatens biodiversity by causing habitat loss, changing the timing of seasonal events (like flowering and migration), and increasing the frequency of extreme weather events. These changes can result in the decline or extinction of species, disrupting entire ecosystems.
What are some examples of how climate change impacts wildlife?
Some examples of how climate change impacts wildlife include the bleaching of coral reefs due to warmer ocean temperatures, the melting of sea ice affecting polar bears' hunting and breeding patterns, and the shifting ranges of birds due to changes in temperature and availability of food.
How can individuals and society help mitigate the impact of climate change on wildlife and ecosystems?
Individuals and society can help mitigate the impact of climate change on wildlife and ecosystems by reducing greenhouse gas emissions through lifestyle changes, supporting renewable energy sources, and advocating for policy changes. Conservation efforts and the protection of natural habitats also play a crucial role in preserving biodiversity.
What are the potential consequences if we do not address climate change's impact on wildlife and ecosystems?
If we do not address climate change's impact on wildlife and ecosystems, we may witness a dramatic loss of biodiversity and the collapse of ecosystems. This can disrupt important ecological processes, such as pollination and nutrient cycling, and have cascading effects on human societies, including impacts on food security and economic stability.
How does climate change affect wildlife and ecosystems?
Climate change affects wildlife and ecosystems in various ways. Rising temperatures can disturb the delicate balance of ecosystems and lead to habitat loss for many species. Changes in precipitation patterns can also impact the availability of water and food resources, affecting the survival and migration patterns of animals. Additionally, climate change can cause the spread of diseases and pests, posing further threats to wildlife populations.



